Retinal Atrophy Frequently Asked Questions

Q: What is Retinal Atrophy?
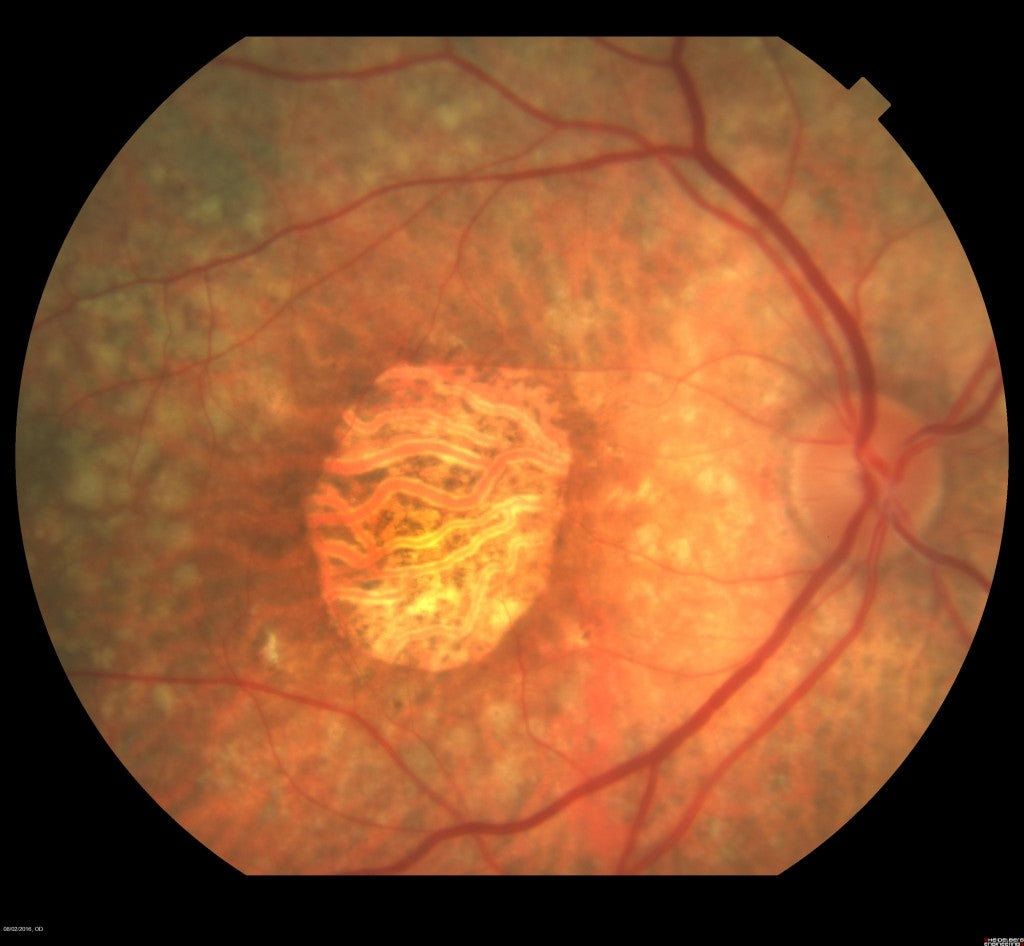
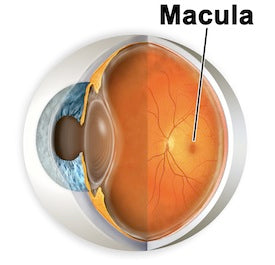
A: Retina health is essential to good vision. Deterioration of the retina is one of the main causes of macular degeneration. Retinal atrophy is a hereditary disorder that can cause permanent blindness. It occurs as a result of the death of photoreceptor cells, commonly called rods and cones, in the eye. It usually occurs in teens, and may cause complete blindness by 40 years old.
Q: What are its symptoms?
A: There are several symptoms, including:
- Night Blindness is one of the first, most common symptoms. The rods in the eye are the first to deteriorate, which are responsible for discerning objects in low light conditions.
- Tunnel Vision typically occurs next; where a person’s peripheral vision is obscured.
- Central Vision loss occurs in the last stages of the disease and accompanies the onset of permanent blindness.
Q: Is retinal atrophy common?
A: About 10, 000 people in just the United States alone suffer from this condition. It can be a result of a genetic mutation in the eye that causes photoreceptor cells to manufacture the wrong protein for the eye. It is also a progressive form of dry macular degeneration that can be resistant to interventions.
Q: I’ve been diagnosed with it. What treatments are available for retinal atrophy?
A: Currently, there is extensive research studying what treatments work to combat the effects. It has been noted that a combination of vitamin A and docosahexaenoic may be of limited benefit.
At VisiVite.com, we carry eye vitamins to support eye health. Check out our Vitamins For Retinal Health to promote healthy vision.
Q: How does it relate to macular degeneration?
A: Scientists at the University College London Institutes of Ophthalmology and Child Health and Moorfields Eye Hospital are conducting research to discover whether transplanting stem cells in retinal atrophy and macular degeneration sufferers can treat both diseases. This can be a major step to finding a cure.